
September 2024 Update on the Sister Study and the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) New medical studies and statements released this year confirm that talcum
Yes, heart injury lawsuits and settlement claims have been filed for IVC plaintiffs. Our firm is filing lawsuits when IVC filters migrate to a patient’s
Traducido por Jose De Jesus Sanchez Un filtro IVC (vena cava inferior) es un dispositivo médico pequeño con forma de cono que comúnmente se implanta
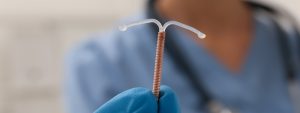
Traducido por Jose De Jesus Sanchez ParaGard se pinta como el aparato contraceptivo perfecto. El dispositivo de cobre Paragard es un contraceptivo que se inserta
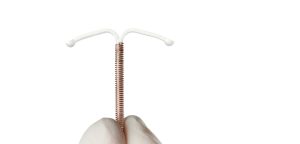
Traducido por Jose De Jesus Sanchez ParaGard, un tipo de aparato intrauterino (DIU) fabricado por Teva Farmacéuticos, ha sido el sujeto de demandas durante años

What is Talcum Powder? Talc/Talcum Powder is a naturally occurring mineral mined from the earth and ground into a fine powder. It is made up

Recent findings from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have brought alarming news to light: ground cinnamon, a staple in many households, is being

Thousands of bottles of ointments for dry eyes, sold in Walmart and CVS stores, are being recalled across the United States due to potential contamination

By Alanna Chen Cinnamon in WanaBana, Schnucks and Weis applesauce has caused many young children around the country to have a high lead blood level,

By Amelia Thorp In the last few months, lead contamination has been a hot topic. Lawsuits for children with lead poisoning are being filed, and

On November 13, 2023, the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) issued a health advisory about a lead recall for cinnamon applesauce pouches. Specifically,
In the last month, three companies have recalled their products because of lead contamination. It is especially concerning, as these fruit puree pouches are commonly
Wanabana, a food company that prides itself on providing the “ideal snack for the whole family”, has recently been under fire after lead was found
On January 30, 2023, a U.S. court rejected[1] Johnson & Johnson’s (J&J) attempt to file for bankruptcy in response to the tens of thousands of lawsuits
A new warning has surfaced for Delsam Pharma’s Artificial Eye Ointment which is an over-the-counter product manufactured by Global Pharma Healthcare Private Limited. The same
Lawmakers are taking notice as more information comes to light about the link between Johnson & Johnsons’ talcum powder and asbestos-related injuries. Recently, U.S. Congressman
The recent news[1] about possible problems with EzriCare Artificial Tears has raised concerns for individuals who have used this product. The Centers for Disease Control and
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration announced the results of a collaborative effort with other government agencies to identify potentially unsafe or tainted dietary supplements.
By:Indhira Benitez As a NYC native now residing in Boston, I often find myself looking for the more “economically efficient” alternatives to traveling back home.
Congress’ 2008 Consumer Product Safety Improvement Act mandates the creation of a searchable product safety database. The public database is being developed by the U.S.
Not long ago, the Toyota Prius was the star of the Japanese automaker’s line-up. With its distinctive appearance and hybrid technology, it was seemingly a
Cigarettes and hoverboards; what do they have in common? Lithium-ion Batteries. Many electronic cigarettes and so called hoverboards use lithium ion batteries because of their
Monsanto, the globally known agriculture chemical company, recently received another blow against them. Monsanto was ordered to pay around $46.5 million to three different plaintiffs
By: Charles Lee St. Jude Medical Inc. has recalled their device, the Amplatzer TorqVue FX Delivery System, and had urged customers and doctors to remove
By: Indhira Benitez As recently reported in the media, Fung Wah’s bus fleet was removed from the roads following inspections by the state Department of
Throughout New York and the rest of the United States, there has been a trend of students using stimulant drugs, originally meant for those suffering
Eva Echeverria had used Johnson & Johnson’s baby powder as part of her feminine hygiene routine since the age 11, unaware of the product’s link
Widely used among consumers of all ages, talcum powder is a popular product found in any drug store. However, the easily accessible product has many
For years, the manufacturers of Johnson’s Baby Powder have fought allegations that the product caused ovarian cancer by calling the evidence “junk science”. Now, that
Johnson & Johnson, the manufacturer of the ever-popular Johnson’s Baby Powder, had appealed an earlier jury verdict that awarded a woman who had contracted ovarian
A New Jersey state judge upheld the $186 million in punitive damages against Johnson & Johnson, the manufacturer of Johnson’s Baby Powder. In the ruling,
Our firm was the first to file NuvaRing suits in state and federal courts. Before any national or global attention was drawn to a higher
A new follow up study by Øjvind Lidegaard found that compared to combined oral contraceptives containing levonorgestrel users of vaginal ring contraceptives (such as NuvaRing)